Top 10 Discoveries at NOIRLab
This list ranks discoveries made with data from telescopes at NOIRLab sites in order of their scientific importance and public appeal.
1. Discovery and Confirmation of Dark Energy and the Accelerated Expansion of the Universe
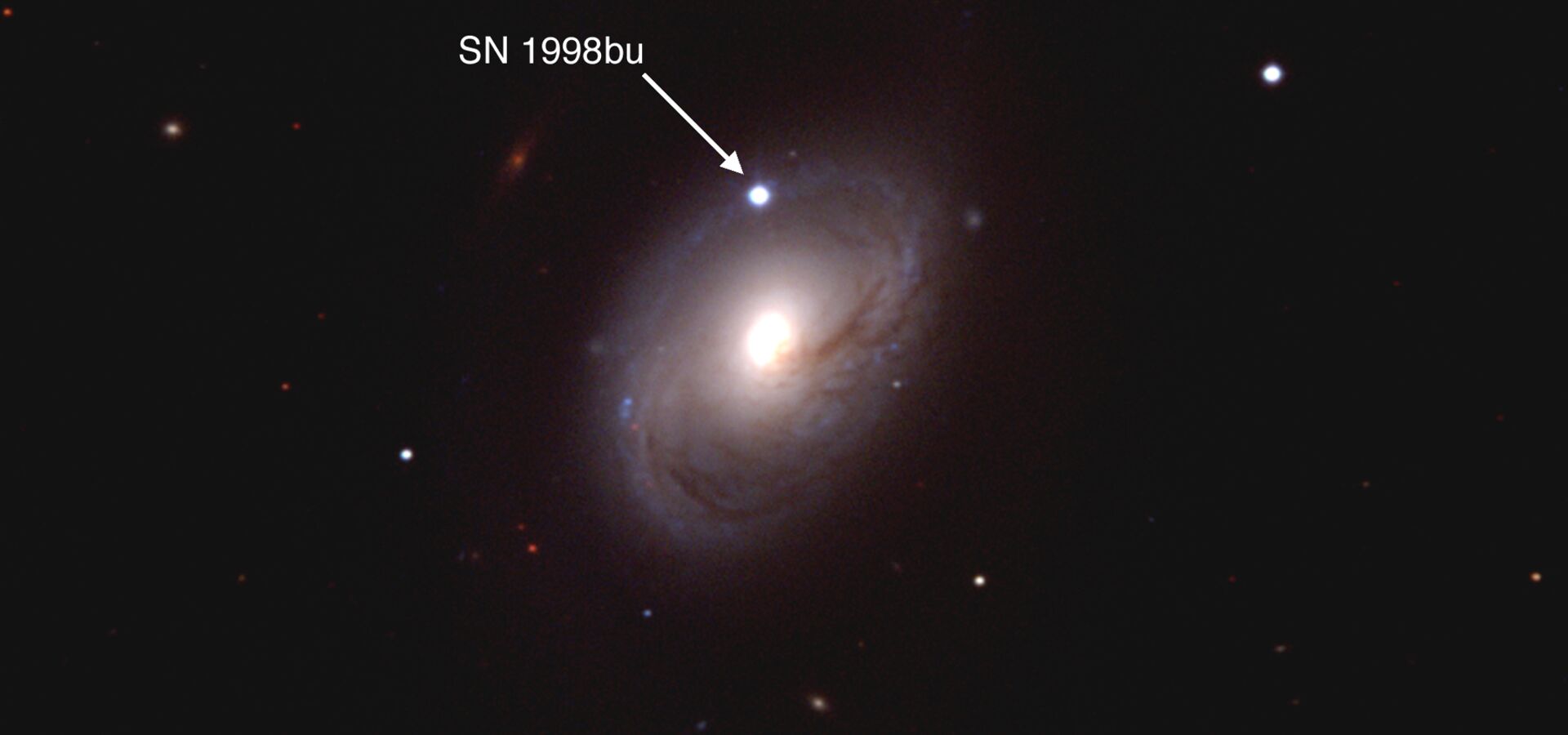
Astronomers discovered the accelerating expansion of the Universe by using Type Ia supernovae as distance indicators. Observations were made using the Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope and Curtis Schmidt Telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, and the WIYN 3.5-meter Telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory. The unexpected discovery led to the concept of dark energy, and contributed to the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics to its discoverers.
Science Papers
"Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant"
"Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae"
Read More
Press Release NOAO9810
Organizational Release NOAO1105
2. First Light from a Gravitational Wave Source
The first-ever detection of a visible-light (and electromagnetic) counterpart to the gravitational wave event GW170817 initiated a time-critical sequence of observations in 2017. Data was obtained using telescopes that included the Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope's Dark Energy Camera (DECam), SOAR Telescope's Goodman Spectrograph, SMARTS 1.3-meter Telescope, Las Cumbres Observatory 1-meter Telescope, PROMPT-5 Telescope, and KMTNet 1.6-meter Telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory; and Gemini South's Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS) and FLAMINGOS-2. The flexibility in their instruments were integral to the limited time frame in this effort.
Science Papers
"Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger"
Read More
Press Release NOAO1705
Press Release Gemini1708
3. Vera Rubin uses Rotation Curves of Distant Galaxies for the Discovery and Confirmation of Dark Matter
Astronomers Vera C. Rubin and W. Kent Ford used the KPNO 2.1-meter Telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory to determine the rotation curve of the Andromeda Galaxy, providing important evidence that contradicted expectations of how matter is distributed inside a spiral galaxy. Subsequent observations were made with the Nicholas U. Mayall 4-meter Telescope at KPNO, and the Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, all together confirming the existence of dark matter.
Science Papers
"Rotation of the Andromeda Nebula from a Spectroscopic Survey of Emission Regions"
Read More
Announcement NOAOAnn16022
4. Testing General Relativity using a Star's Redshift around Sagittarius A*
In March–September 2018, the star S0-2 came at its closest approach to the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* at the center of our Milky Way, allowing a novel test of general relativity by measuring its gravitational redshift. Observations with Gemini North's Near Infrared Integral Field Spectrometer (NIFS) provided critical year-long spectral measurements of S0-2's speed at its closest approach, confirming that the redshift was consistent with general relativity. This work contributed to the 2020 Nobel Prize.
Science Papers
"Monitoring Stellar Orbits Around the Massive Black Hole in the Galactic Center"
Read More
Announcement GeminiAnn19004
5. World's largest 3D map of the Universe
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) on the Nicholas U. Mayall 4-meter Telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory has created the world's largest 3D map of the Universe. Initial analysis of the first-year data with the highest precision ever, providing an unprecedented look at the nature of dark energy and its effect on the Universe's large-scale structure.
Science Papers
Adame, A. G., Aguilar, J., Ahlen S., et al. 2024
Read More
NOIRLab Press Release Link
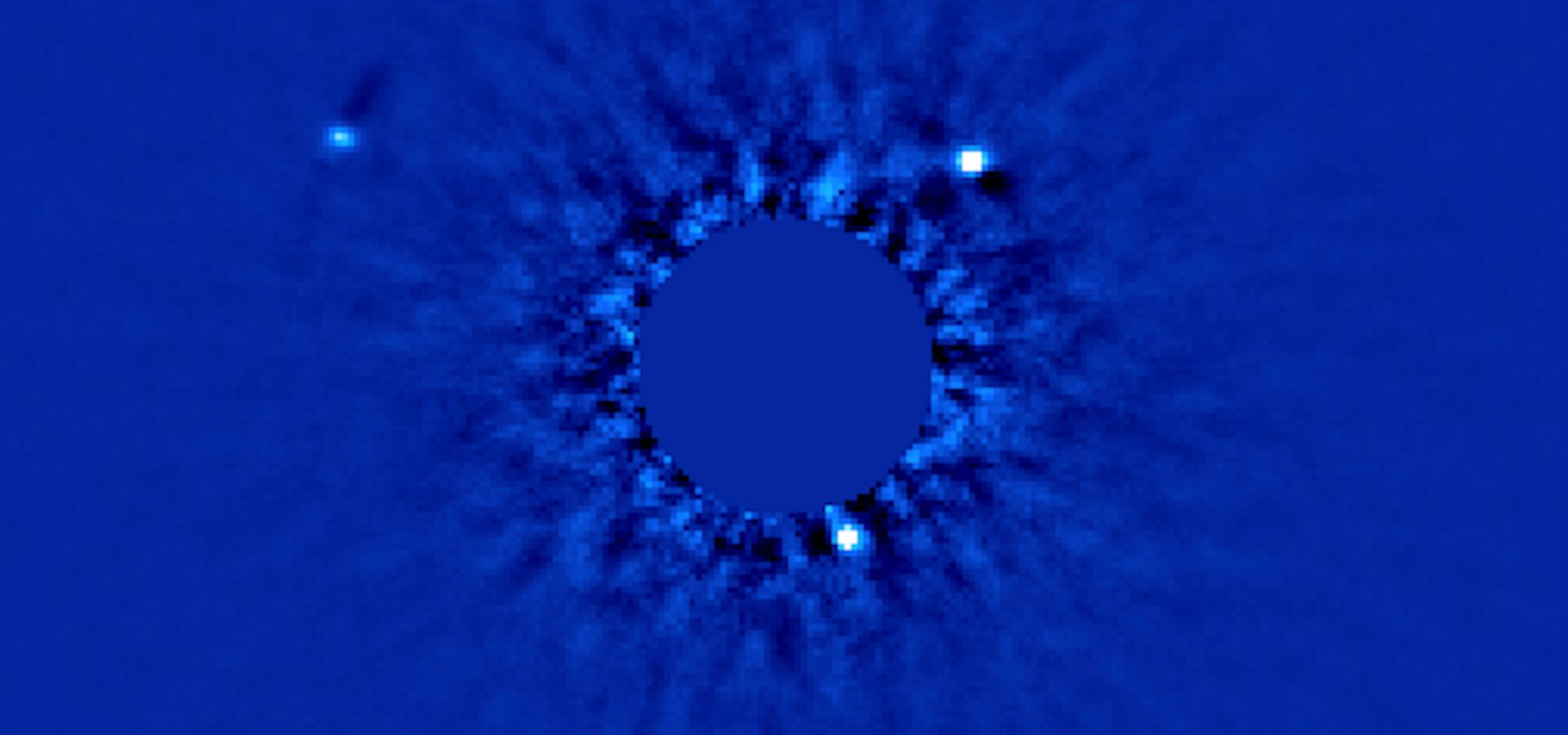
6. First Direct Images of a Multi-Planet System Orbiting a Star
Astronomers using Gemini North's ALTtitude conjugate Adaptive optics for the InfraRed (ALTAIR) and Near-Infrared Imager (NIRI), and W.M. Keck Observatory on Hawai‘i’s Maunakea, obtained the first-ever direct images identifying a multi-planet system. The Gemini images of the star HR 8799 show three planets in the confirmed planetary system.
Science Papers
"Direct Imaging of Multiple Planets Orbiting the Star HR 8799"
Read More
NOIRLab Press Release Gemini0808
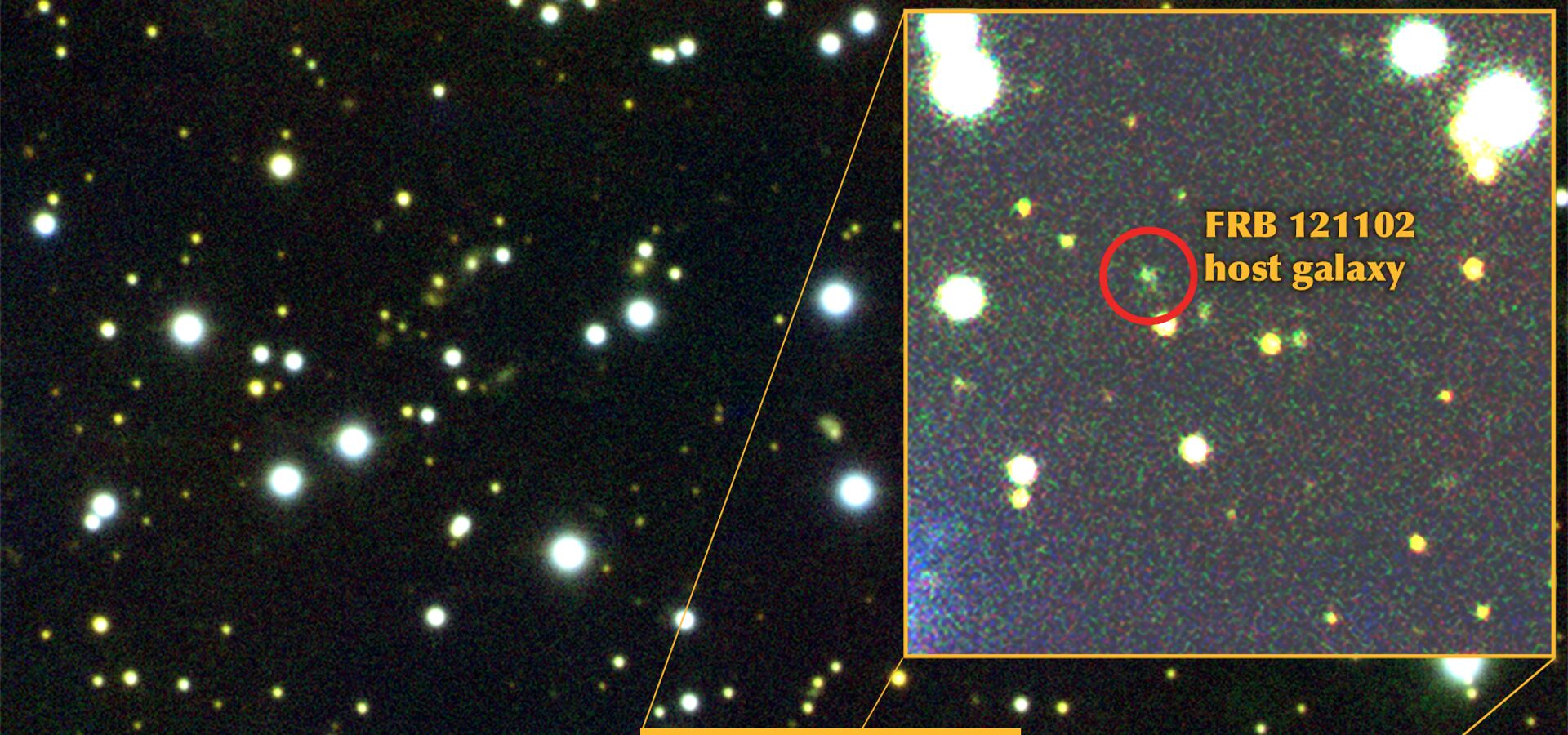
7. Direct Localization of a Fast Radio Burst and its Extragalactic Host
The first optical localization of the Fast Radio Burst (FRB) 121102 was made using Gemini South's Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS). Its repeating nature allowed astronomers to localize the Fast Radio Burst in a distant dwarf galaxy, contrasting the belief that most Fast Radio Bursts come from large galaxies.
Science Papers
"A direct localization of a fast radio burst and its host"
"The Host Galaxy and Redshift of the Repeating Fast Radio Burst FRB 121102"
Read More
NOIRLab Press Release Gemini1701
8. Discovery of a Luminous Quasar powered by a Gigantic Supermassive Black Hole in the Early Universe
Using the Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope's Dark Energy Camera (DECam) at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, and Gemini North's Gemini Near-Infrared Spectrograph (GNIRS), astronomers discover a luminous quasar named Pōniuāʻena powered by an extreme supermassive black hole. Scaling over one billion solar masses, the SMBH's existence at just 700 million years after the Big Bang significantly challenges current models of earliest SMBH growth.
Science Papers
"Pōniuā'ena: A Luminous z = 7.5 Quasar Hosting a 1.5 Billion Solar Mass Black Hole"
"An 800-million-solar-mass black hole in a significantly neutral Universe at a redshift of 7.5"
Read More
Press Release NOIRLab2015
9. First Direct Evidence of Gravitational Lensing
Two very close quasistellar objects (now called quasars) were discovered in 1979 with nearly identical spectral characteristics. Astronomers assumed their initial conditions must be similar, but found that they were in fact two images of the same object produced by a gravitational lens. Observations were made using the KPNO 2.1-meter Telescope and UArizona Bok 2.3-meter Telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory.
Science Papers
"0957+561 A, B: twin quasistellar objects or gravitational lens?"
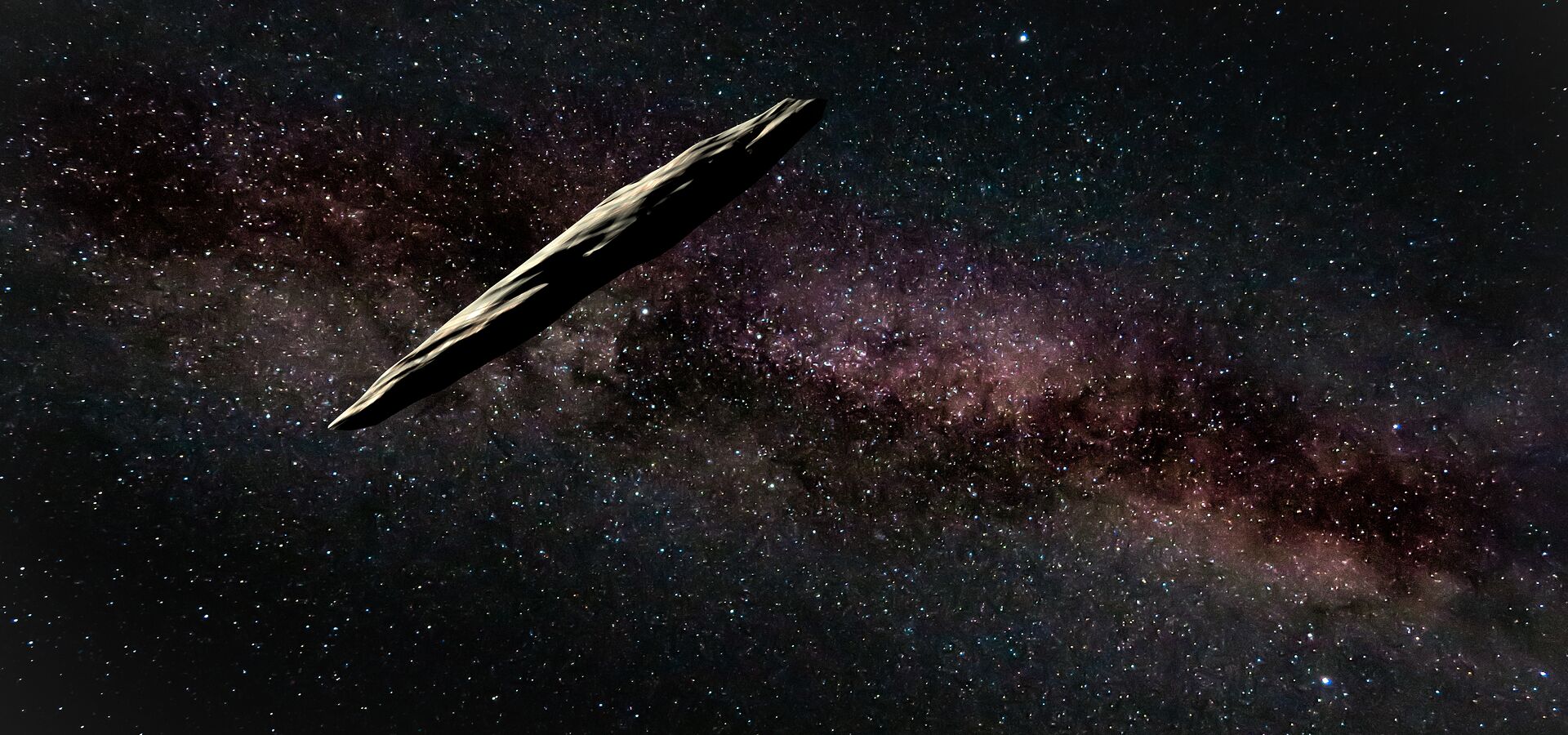
10. Interstellar Asteroid 'Oumuamua with Extreme Oblong Shape visits Solar System
‘Oumuamua, the first extrasolar object discovered and with a dramatically unprecedented oblong shape, briefly visits the Solar System as found by Gemini South's Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS). Light-curve observations provided clues to its asteroidal nature and origin, suggesting that previous estimates of the number density of interstellar objects were very low.
Science Papers
"A brief visit from a red and extremely elongated interstellar asteroid"
"Non-gravitational acceleration in the trajectory of 1I/2017 U1 (‘Oumuamua)"
Read More
Press Release Gemini1710