Probing the host galaxy of a luminous quasar
1 July 2008
Probing the Host Galaxy of a Luminous Quasar with Gemini Laser Adaptive Optics
A team led by Linda C. Watson, Ph. D. student at the Department of Astronomy, Ohio State University, has made the first bulge stellar velocity dispersion measurement of a luminous quasar host with the Gemini North Laser Guide Star adaptive optics system. The target quasar was PG1426+015, about 1.36 billion light-years away (Figure 1). This result is also the basis for the 500th refereed paper based on Gemini observations.
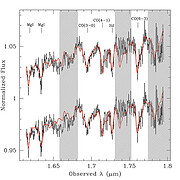
They employed the spectro-imaging spectrograph NIFS fed by the Gemini facility adaptive optics system Altair to obtain high signal-to-noise ratio measurements of near-infrared Si I and Mg I lines and also several CO bandheads in the quasar host galaxy spectrum of PG 1426+15 (Figure 2). Using these measurements, the team found a stellar velocity dispersion of 217 +/- 15 kilometers/second in the region of the galaxy between 0.1'' and 1'' (520 light-years and 5,200 light-years) from the galaxy's center.
The NIFS integral field unit and the laser guide star adaptive optics system are well suited for host studies of luminous quasars. The bright quasar at the center of the galaxy outshines the stars in the host. But with adaptive optics, the authors could confine that diluting quasar light to the very center of the image and simply exclude it from their spectrum. The integral field unit then allowed them to gather more stellar light from the host galaxy than would have been possible with a normal single-slit spectral observation.
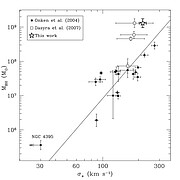
Using their derived velocity dispersion (σ*), the authors found that PG 1426+015 lies significantly above the MBH - σ* relation for active galactic nuclei (Figure 3), where MBH is the mass of the black hole powering the quasar. One possible reason for this is that high-luminosity quasars—like PG1426+015—might have disks of gas around their central black holes that have different inclinations compared to lower luminosity quasars. To determine whether all high-luminosity quasars lie above the MBH - σ* relation and why, the authors propose observations of more hosts of high-luminosity quasars with NIFS and Altair.
Finally, not only did the team make a precise measurement of the central bulge velocity dispersion, but they also found a surprisingly young stellar population in this quasar host.
For more details, see the article "First stellar velocity dispersion measurement of a luminous quasar host with Gemini North Laser Guide Star adaptive optics," by Linda C. Watson, Paul Martini, Kalliopi M. Dasyra, Misty C. Bentz, Laura Ferrarese, Bradley M. Peterson, Richard W. Pogge and Linda Tacconi, The Astrophysical Journal, 2008, Accepted. As noted earlier, this article is the 500th refereed Gemini paper.
Links
- First stellar velocity dispersion measurement of a luminous quasar host with Gemini North Laser Guide Star adaptive optics. A pre-print of the article can be found on astro-ph.