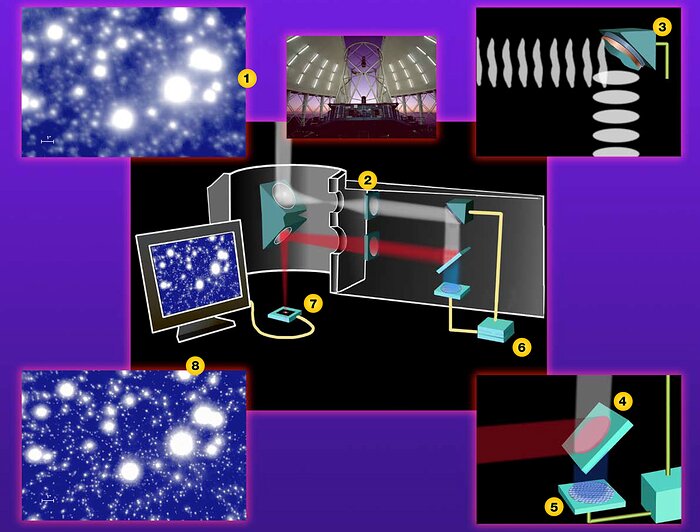
How Adaptive Optics (AO) Works
The illustration (1) is an example of an image (NIRI H-band image at 0.26 arcsec natural seeing) without the help of adaptive optics. When starlight is collected and focused by telescope, just prior ro coming to a focus, the light entering an adaptive optics system is first collimated (2) and is reflected off a deformable mirror (3). After reflecting off the deformable mirror, the light passes through a beam-splitter (4) where the shorter wavelength light (optical) enters the wavefront sensor (5) wich takes a "snapshot" of the distortions on the wavefront and sends the information via computer (6) back to the deformable mirror to adjust the wavefronts and keep them flat. Finally, the light is focused (7) and imaged on a detector (8) (NIRI/Altair H-band AO-corrected image at 0.060 arcsec) for astronomers to study.
Créditos:International Gemini Observatory
About the Image
| Id: | gemini0301b |
| Tipo: | Collage |
| Release date: | 2 de Junio de 2003 a las 20:00 |
| Related releases: | gemini0301 |
| Size: | 1752 x 1332 px |
Sobre el Objeto
| Categoría: | Illustrations |