Gemini South Adaptive Optics Imager (GSAOI)
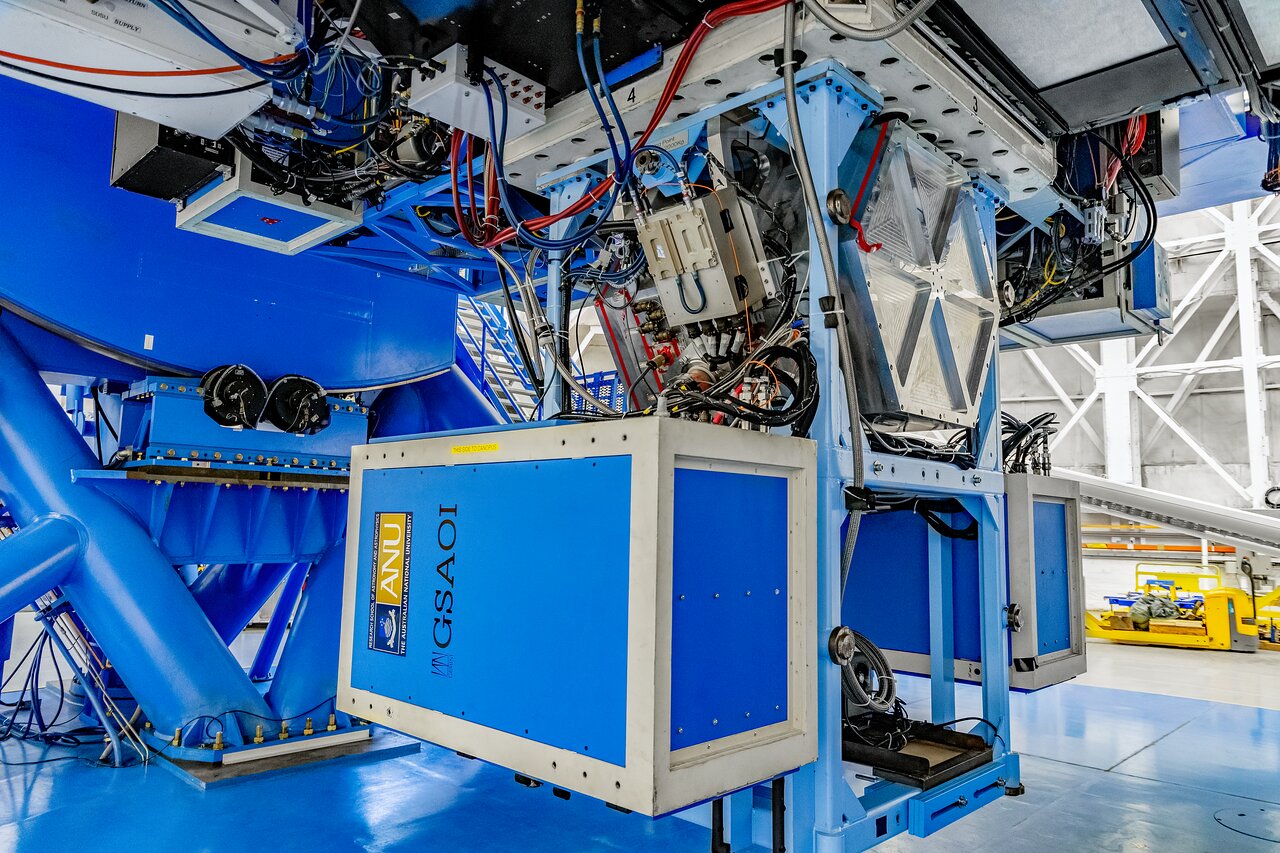

Gemini South Adaptive Optics Imager (GSAOI) on Gemini South.
Credit: CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/D. Munizaga
The Gemini South Adaptive Optics Imager (GSAOI) is a near-infrared adaptive optics imager built by the Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics (RSAA) of the Australian National University and designed to be used with the Gemini Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics System (GeMS) at Gemini South. It can deliver nearly diffraction-limited images in the wavelength interval 0.9–2.5 μm over a 85 x 85-arcsecond field of view. The GSAOI detector is formed of four 2048 x 2048 Rockwell HAWAII-2RG pixel arrays that form a 4080 x 4080-pixel focal plane. There are four gaps of about 2.5 millimeters between the arrays, corresponding to approximately 2.4 arcseconds on sky. Each array has an additional four rows and columns around the outer edges that read out as reference pixels and are not illuminated.
GSAOI contains two filter wheels and one utility wheel.The two filter wheels have 22 broad- and narrow-band (zero-redshifted) emission- and absorption-line filters installed. Each filter wheel also contains one blocked position for recording bias and dark frames. The utility wheel contains a pupil viewer and two defocus lenses (convex and concave). The pupil viewer is used to accurately align the cold stop with GeMS exit pupil viewer and so minimize the background reaching the imager detector. The GSAOI Integration Time Calculator (GSAOI ITC) — a web form in which the user defines the principal aspects of the observation — can be used to determine limiting magnitudes, exposure times, signal-to-noise ratios, background levels, etc. for a wide range of source properties, observing conditions, and GSAOI configurations.
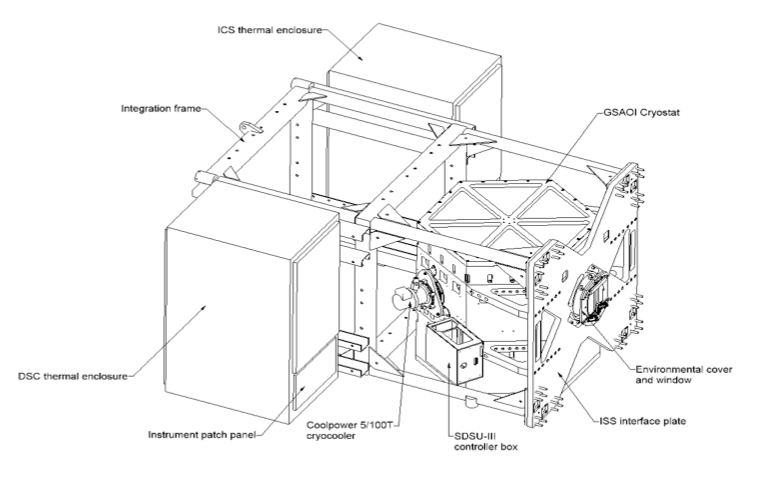 GSAOI internal design graphic.
GSAOI internal design graphic.
Science Highlights of GSAOI
- Astronomers Witness Star Devouring Planet: Possible Preview of the Ultimate Fate of Earth
- Sidewinding Young Stellar Jets Spied by Gemini South
- Looking Sharp: Most Detailed Image Yet of Famous Stellar Nursery
- Ultra-sharp Images Make Old Stars Look Absolutely Marvelous!
- Cluster’s Advanced Age in Razor-sharp Focus
- Ultra-sharp Image Uncovers the Shocking Lives of Young Stars
Quick Facts
|
|
Gemini South Adaptive Optics Imager (GSAOI) For scientists: Please find the most up-to-date details about the instrument offerings on the Gemini website. |
|
|---|---|
|
Site |
Cerro Pachón |
|
Telescope |
Gemini South |
|
Type |
Imager |
|
Wavelength range |
0.9–2.4 μm |
|
Spatial sampling |
0.02 arcseconds per pixel |
|
Number of detectors |
4 Rockwell HAWAII-2RG arrays (2048 x 2048 pixels each) |
|
Detector format |
4 arrays arranged 2 x 2 |
|
Detector total size |
4080 x 4080 pixels |
|
Field of view |
85 x 85 arcseconds |
|
Filters |
|
|
Date of first light |
16 December 2011 |
|
Science Goals |
The science goals are directly related to the Gemini Multi-Conjugate Adaptive Optics System (GeMS) Examples include: The evolution of the mass function of stars in the Milky Way and the Magellanic Clouds History and evolution of star formation in nearby galaxies Star formation history of distant galaxies |
|
Images taken with the instruments |
|
|
Images of the instrument |
|
|
Videos of the Instrument |
|
|
Press releases with the instrument |
|